Topical Minoxidil for Hair Loss
Hair loss and hair shedding are frustrating to experience, but you are not alone. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, an estimated 80 million Americans are affected by androgenetic alopecia, a medical condition resulting in hereditary thinning or baldness due to an imbalance of androgen hormones. If you are experiencing hair loss and are interested in starting medications such as topical minoxidil, Dr. Green is here to help. Dr. Michele Green is a board-certified dermatologist with over 25 years of experience with male-pattern baldness and female-pattern hair loss. In her private Upper East Side NYC dermatology office, she will assess your hair concerns and medical history to determine an individual treatment plan for hair rejuvenation.
Topical minoxidil is an FDA-approved medication used to treat androgenetic alopecia-related hair loss in both men and women. Topical minoxidil keeps hairs in the growth phase, reducing shedding and promoting hair growth and retention. Additionally, minoxidil increases blood flow to the scalp, carrying oxygen and nutrients necessary for hair growth to hair follicles. Topical minoxidil can be found over the counter in various strengths and forms. While topical minoxidil is currently approved for treating androgenetic alopecia, it can be used off-label in individuals suffering from other causes of hair loss, such as alopecia areata or telogen effluvium. With consistent use, topical minoxidil has proven to be an effective treatment for hair loss.
Dr. Michele Green treats all types of hair loss, from androgenetic alopecia to autoimmune disorders and hormone imbalances. Dr. Green is an expert in medical and cosmetic hair loss treatments and was one of the first providers in New York to offer plasma-rich platelet (PRP) injections to treat hair loss in both men and women. When treating hair loss, Dr. Green may prescribe serums such as topical minoxidil in addition to various oral medications and in-office treatments, depending on the type and cause of hair loss. Dr. Green is an internationally renowned board-certified dermatologist and has consistently been voted as a top NYC dermatologist by Castle Connolly, New York Magazine, Super Doctors, and The New York Times due to her dedication to her patients.
What is topical minoxidil?
Topical minoxidil, more commonly known by its brand name, Rogaine, is a medication used to stimulate hair growth in men and women. Topical minoxidil was first approved in 1988 by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for hair loss caused by androgenetic alopecia in men, followed by an approval in 1992 for use in women experiencing androgenetic alopecia-related hair loss. Minoxidil is classified as a vasodilator medication as it dilates or opens blood vessels, leading to an increase in circulation and a decrease in blood pressure. While providers first prescribed minoxidil to treat high blood pressure, it is now one of the most effective treatments for hair loss.
It is unclear exactly how minoxidil works to increase hair growth and retention. Currently, minoxidil is thought to affect the amount of time that hair strands stay in various stages of hair growth. There are four stages to hair growth: the anagen (growing) phase, the catagen (transition) phase, the telogen (resting) phase, and the exogen (shedding) phase. Minoxidil likely accelerates the telogen phase, decreasing hair fallout and causing hair to enter and stay in the anagen, or growth phase, for longer periods. Additionally, the improvement of circulation due to minoxidil’s vasodilatory effects may contribute to more oxygen and nutrients being delivered to hair follicles in the treated area. Continued daily usage of topical minoxidil will combat hair thinning to result in thicker, fuller hair.
What is androgenetic alopecia?
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly referred to as male-pattern baldness or female-pattern hair loss, is a hereditary condition that contributes to hair loss due to androgen hormone imbalances. Increased levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) bind to and destroy hair follicles at the scalp. In men, androgenetic alopecia presents as a thinning crown and receding hairline, creating the classic “M” shape at the hairline. In women, androgenetic alopecia presents as thinning hair that contributes to a widening part and hair loss around the top of the head. While topical minoxidil is only FDA-approved to treat hair loss related to androgenetic alopecia, it has also been used off-label to treat other causes of hair loss. Two common causes include alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition in which healthy hair follicles are attacked by the body’s immune system, and telogen effluvium, hair loss characterized by rapid shedding due to sped-up telogen and exogen phases.
How do you use topical minoxidil?
Minoxidil topical solution comes in two formulations, a liquid solution or a foam, and can be purchased at strengths of either 2% or 5%. Clinical trials have shown that the foam and solution forms of minoxidil are equally effective at promoting hair growth and retention – choosing the topical form to purchase will depend on user preference. Hair should be completely dry before applying topical minoxidil. Remove the caps from the bottle and apply the recommended amount of topical solution or foam to the areas most affected by hair thinning or loss, massaging gently into the scalp. After massaging, immediately wash your hands with soap and water to remove any excess minoxidil from the hands.
You should wait for the minoxidil to dry on the hair before applying any styling products or heat. Individuals typically use topical minoxidil twice daily, although it is important to follow the instructions located on your minoxidil product. Topical minoxidil should be kept at room temperature and away from excess moisture and heat. If you accidentally skip a dosage, do not use more than the prescribed amount to make up for the missed dose; instead, continue with your regular, next dose.
Who should not use topical minoxidil?
Topical minoxidil should not be used by pediatric individuals or individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding, as its effects on these individuals have not been determined. Inform your doctor if you are using any other prescription or nonprescription medications before using minoxidil. Although there have been no reported drug interactions to date, high blood pressure medications like guanethidine and erectile dysfunction drugs or medications that interact with alcohol, such as disulfiram or metronidazole, may interact with minoxidil. Tell your doctor if you have any allergies to topical ingredients, as topical minoxidil may contain inactive ingredients that can cause allergic reactions. Medical conditions such as hypertension, heart disease, kidney disease, liver disease, or skin issues such as eczema, infection, or scalp irritation can also affect the use of minoxidil. It is important to consult with your doctor or dermatologist if you are interested in using topical minoxidil to ensure it is safe to use.
Why can’t over 65s use minoxidil?
The FDA has not approved topical minoxidil usage in individuals aged 65 and over, as its effects have not been studied. However, individuals can use it off-label for hair loss. If you are over 65 years old and are considering topical minoxidil treatment, consult with a board-certified dermatologist such as Dr. Green to ensure treatment is safe and effective for you.
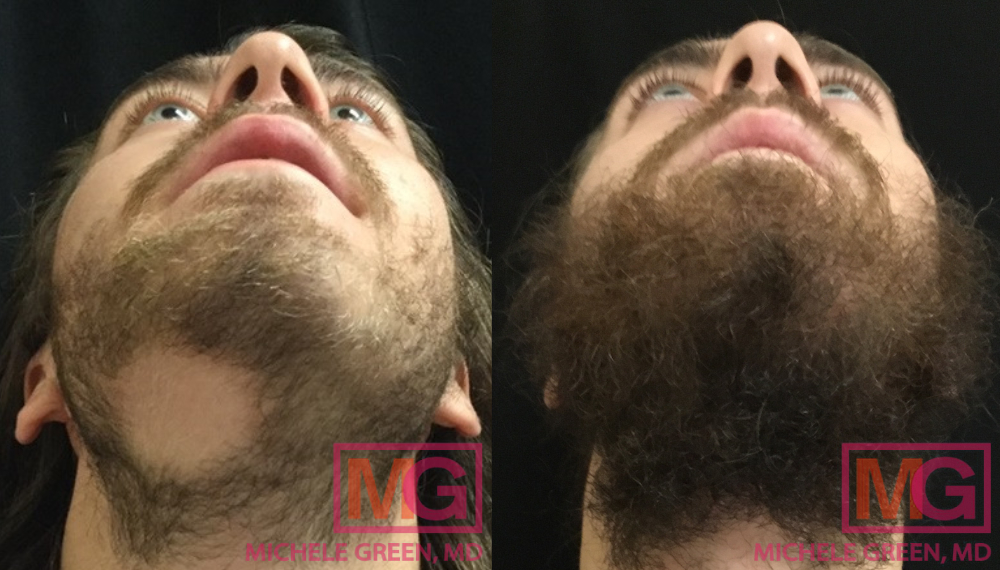

Can minoxidil regrow hair in bald spots?
Unfortunately, minoxidil will not be able to regrow hair in completely bald spots. In order for minoxidil to work, active hair follicles must be present in the area. A bald spot indicates that the hair follicles in the area have died, eliminating any chance of hair regrowth. If you are experiencing bald spots due to alopecia areata, topical minoxidil may be an effective, off-label treatment. During a consultation with Dr. Green, she will be able to assess your hair and bald spots to determine if topical minoxidil is right for you.
Why is my hair thinning after using minoxidil?
Hair thinning or shedding can occur when starting topical minoxidil, though this side effect differs between patients. This effect, known as topical minoxidil shedding, likely occurs because minoxidil is thought to accelerate the later stages of hair growth to increase the length of time that your hair is in the growth hair. While this effect is great for hair growth, it can initially cause your hair to shed. After consistently using topical minoxidil for a few months, hair thinning should decrease as new hair growth sets in. If you are noticing a large amount of thinning, you can reduce the dosage of minoxidil and work up to a more powerful dose.
How long does topical minoxidil shedding last?
It is hard to say exactly how long topical minoxidil shedding may last. Topical minoxidil shedding typically starts after initial usage and continues for about two to four months. Hair growth should then begin to occur, and the shedding should decrease. If shedding still occurs four months after consistent usage of topical minoxidil, schedule a consultation with a dermatologist such as Dr. Green about alternative treatment options, as the thinning may be unrelated to minoxidil.
What are the side effects of topical minoxidil?
Common side effects of topical minoxidil include skin irritation such as itching, dryness, or skin rash. Some individuals have reported changes in hair color and texture after continued usage of minoxidil. Serious side effects are rare but can include hypertrichosis or unwanted facial or body hair growth, lightheadedness, fast or irregular heartbeat, burning, acne in the treatment area, chest pain, swelling, rapid weight gain, and trouble breathing. If you experience any of these adverse effects, immediately discontinue usage and inform your doctor for medical advice. While allergic reactions to topical minoxidil are rare, seek medical attention immediately if you experience symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as a rash, swelling of the face, tongue, or throat, trouble breathing, or dizziness. You can report any side effects to the FDA at www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Does hair become dependent on Minoxidil?
Your hair itself will not become dependent on minoxidil, but the growth observed during treatment is dependent on Minoxidil usage. Minoxidil works to keep hair in the anagen, or growth stage, to decrease hair loss and promote hair retention and growth. Individuals can maintain the effects of Minoxidil with continued daily usage. However, once minoxidil treatment has stopped, these effects wear off, and your hair will return to its state before minoxidil usage.
When is it too late to use minoxidil?
Individuals experience hair loss at different ages, and it is important to understand the type of hair loss you suffer from in order to determine the most effective treatment. Minoxidil is most effective for those experiencing hair thinning or loss and is most effective in individuals under 40 years of age with recent hair loss. Unfortunately, minoxidil cannot help regrow hair once an area has become bald, as active hair follicles need to be present for the medication to work. If you are deciding if topical minoxidil is right for you, consult with a board-certified dermatologist such as Dr. Green, who can assess your hair and create a customized hair loss treatment plan.
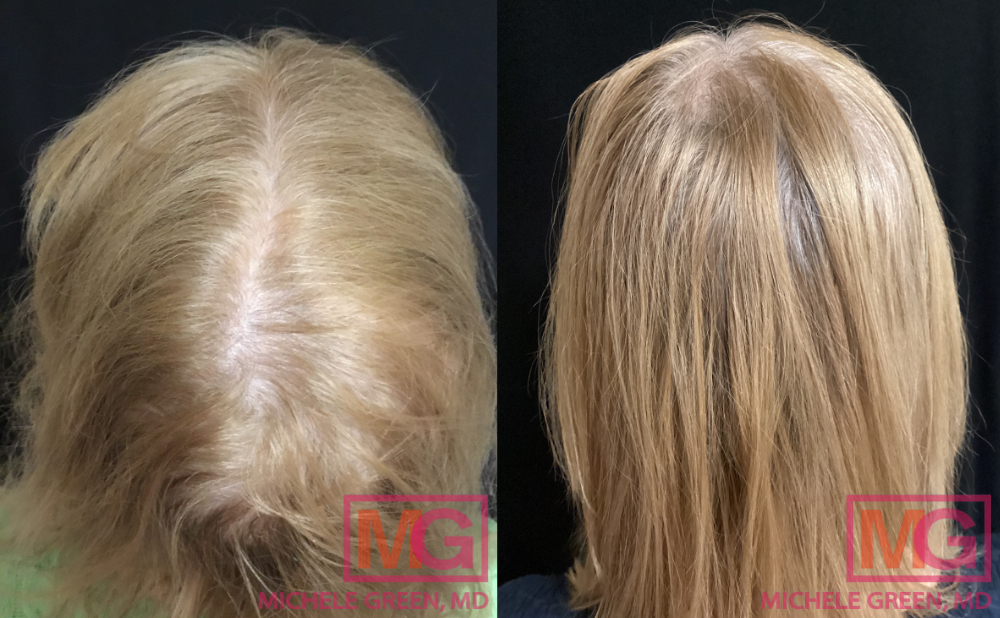
Is topical minoxidil worth it?
Absolutely! Topical minoxidil is an excellent treatment option for those experiencing hair loss or thinning. The medication is affordable and easy to obtain over the counter. Most individuals see an increase in hair growth over time and experience minimal, if any, side effects. It is important to note that topical minoxidil is only effective when used consistently – discontinuing the medication will result in returned hair loss.
Which is better, Rogaine or Minoxidil?
Minoxidil is actually the active ingredient found in Rogaine! Rogaine became the first FDA-approved topical brand for hair loss in both men and women. They carry products over-the-counter with 5% minoxidil for both men and women, as well as a 2% minoxidil solution for women. Their products come as a foam or a solution, depending on your preference of application. Studies have proven Rogaine to be effective for treating hair loss when used consistently.
How do I stop Minoxidil without losing my hair?
Unfortunately, if you stop using minoxidil, the hair shedding and thinning you experienced before starting treatment will start again. Minoxidil works to increase the length of time that hair is in the growing stage – when you discontinue minoxidil, that signal is lost, and hair loss will resume a few months later. If you are thinking about stopping minoxidil, it is essential to consult with a board-certified dermatologist such as Dr. Green to determine alternative treatment options.
Why is Minoxidil not permanent?
Minoxidil works to stimulate hair growth, keeping hairs in the growth stage to increase hair retention and growth. Once minoxidil usage is discontinued, the stimulation to the hair follicles is lost. Without signaling from Minoxidil, hairs will return to their normal growth pattern, and you may lose the hairs that you gained as a result of using Minoxidil.
Why can’t over 50s use Rogaine?
If you are 50 years old, you can use Rogaine, as it is FDA-approved for ages 18 – 65. The efficacy of the treatment for your hair will depend on the type of hair loss you have and what the current state of your hair is. If you are unsure if Rogaine or topical minoxidil is the right choice for you, consult with Dr. Green in her private dermatology office to create a customized hair loss treatment plan for you.
Which vitamin deficiency causes hair fall?
Deficiencies in B vitamins such as biotin, folate, riboflavin, and vitamin B12 have been associated with hair loss. These B vitamins are necessary for the body to convert carbohydrates to glucose, which can then be used to produce energy. While it is rare to be deficient in biotin or riboflavin, folate and vitamin B12 deficiencies are common and can lead to anemia or decreased red blood cells. Red blood cells are extremely important for carrying oxygen to all the cells throughout the body. Without a steady supply of oxygen, hair follicles will not have the necessary nutrients for hair growth. Many over-the-counter hair supplements contain B vitamins such as biotin.
Iron deficiency has also been associated with hair loss and is very common in women with heavy periods and those with vegetarian diets. Iron is a precursor for hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen throughout the body, including hair follicles. Hair follicles need oxygen and nutrients in order to maintain healthy hair growth. An iron deficiency can result in decreased oxygen flow to hair follicles, leading to hair loss. Consuming iron-rich foods such as meat, poultry, fish, and beans are all great options for combating iron deficiency. Your healthcare provider can also prescribe iron supplements if you are iron deficient.
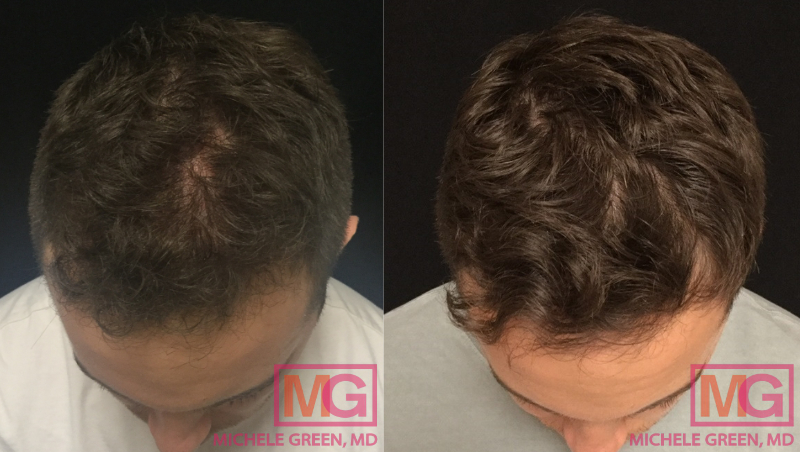
6 months before and after PRP
Is rosemary better than minoxidil?
Rosemary oil contains carnosic acid, a chemical compound with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. When applied to the scalp, rosemary oil is thought to increase circulation, bringing necessary nutrients and oxygen to hair follicles needed for hair growth. Rosemary oil can also decrease inflammation and irritation on the scalp, reducing the development or exacerbation of dandruff. Topical minoxidil was FDA-approved in 1998 and has since been proven to be a safe and effective treatment for hair loss. While rosemary oil is considered beneficial to hair and scalp health, scientists are currently conducting studies comparing the efficacy of rosemary oil to minoxidil, with limited data suggesting that rosemary oil is just as effective as a 2% minoxidil solution. If you are considering using rosemary oil or topical minoxidil for hair loss treatment, consult with a dermatologist such as Dr. Green to generate a customized hair loss treatment plan best suited for you.
What do dermatologists prescribe for hair loss?
There are various medications that dermatologists can prescribe for hair loss. Apart from minoxidil, topical treatments can be formulated with finasteride. Finasteride is a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor and works by decreasing dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels, leading to reduced miniaturization of hair follicles and increased hair density. Some over-the-counter brands carry topical serums containing both finasteride and minoxidil for more comprehensive treatment.
Finasteride can also be prescribed as an oral medication, better known as Propecia. Propecia was FDA-approved in 1997 to treat androgenetic alopecia in both men and post-menopausal women. While Propecia is the only oral medication FDA-approved for hair loss, other medications, such as minoxidil and dutasteride, can be prescribed off-label. Low-dose oral minoxidil, normally used to treat hypertension, has been proven to be a safe and effective treatment option for hair loss. Dutasteride (Avodart) is a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor commonly prescribed for prostate hypertrophy but can be prescribed to decrease DHT levels and reduce hair loss in men. Lastly, spironolactone is an FDA-approved medication used to treat androgenetic alopecia and PCOS in women, as it slows the production of androgens or male sex hormones.
Apart from medications, dermatologists can treat hair loss with platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections. PRP injections are an excellent, innovative treatment and currently the only non-invasive procedure available for hair loss. During the procedure, your blood is drawn and spun in a centrifuge to separate the plasma from other blood components. The PRP contains important growth factors, a mixture of proteins and cytokines, necessary for stimulating hair follicles and promoting hair growth and retention. Typically, individuals benefit from 4 treatment sessions spaced one month apart, along with maintenance sessions to retain hair growth and prevent future hair loss. PRP injections can be completed in conjunction with oral and topical hair loss medications for a more comprehensive treatment plan. Consulting with a board-certified dermatologist such as Dr. Green is best to determine if other oral medications or PRP injections can be effective for you.
Getting started with topical minoxidil treatment today
Hair shedding or thinning can be frustrating and confidence-destroying for men and women alike. Luckily, there are many treatments available to help reduce hair loss and promote hair growth and retention. Topical minoxidil is a proven safe and effective hair loss treatment for men and women experiencing androgenetic alopecia. However, individuals have found success using topical minoxidil off-label for other types and causes of hair loss. Identification of the type and cause of your hair loss is necessary for creating an effective treatment plan for hair revitalization. If you are interested in getting started with topical minoxidil treatment, consult with a board-certified dermatologist such as Dr. Green to ensure that treatment is safe and effective for you.
Dr. Michele Green is an expert in diagnosing and treating hair loss and has helped thousands of men and women with hair loss problems over the last two and a half decades. During your consultation in her private NYC Upper East Side dermatology office, she will assess your hair state, concerns, and medical history to determine an individualized treatment plan. She has consistently been rated as a top NYC dermatologist by Castle Connolly, New York Magazine, Super Doctors, and The New York Times due to her expertise and dedication to her patients. With over 25 years of experience in hair loss treatments, Dr. Green will employ a range of topical haircare, oral medications, and in-office treatments to revitalize your hair and promote new, beautiful, healthy hair growth. Please contact us online today or call 212-535-3088 to learn more about Dr. Green’s personalized approach to hair loss treatment.
 212-535-3088
212-535-3088