What Causes Melasma?
Read About Melasma Causes, Along With Treatment & Prevention
Melasma is a chronic skin condition characterized by patches of brown or gray-brown skin. It results from an overproduction of melanin in specialized cells within the skin, specifically melanocytes (cells that produce melanin). This condition can be exacerbated or triggered by various factors and is more common in women than men. Although melasma is harmless, many patients feel self-conscious about these pigmented patches. Fortunately, various treatments and topical skincare products are available to help manage melasma. When addressing melasma, it is essential to consult a board-certified dermatologist. Dr. Green has over 25 years of experience treating patients of all skin types and tones with melasma. She will utilize her expertise to determine the underlying cause of your condition and develop a personalized treatment plan to help you achieve clear, radiant skin.
The exact cause of melasma remains unknown. Melasma may have a genetic component, as many individuals affected by it have a family history of the condition. Hormones play a significant role in the development of melasma, with increased levels of estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy or the use of hormonal contraceptives linked to its emergence. Photosensitizing medications, such as certain oral antibiotics and cardiac drugs, can trigger or worsen the condition. Sun exposure is the primary trigger for melasma, as UV rays prompt melanocytes to produce more melanin and pigment in the skin. Regardless of the cause of your melasma, Dr. Green will help you find the best combination of in-office treatment options and specially formulated skincare products to enhance your complexion beyond its previous appearance.
Dr. Michele Green is an internationally renowned, board-certified cosmetic dermatologist with over two and a half decades of experience providing some of the world’s most discerning individuals with the best non-invasive treatment options available, including Cosmelan peels for melasma. She is consistently recognized as one of New York City’s top dermatologists by Super Doctors, Castle Connolly, New York Magazine, and The New York Times for her dedication to her patients and her expertise. Dr. Green specializes in treating melasma and other forms of pigmentation resulting from numerous potential triggers. Whether the melasma is caused by the mask of pregnancy, laser treatments, or ultraviolet light combined with birth control pills, Dr. Green has successfully treated these forms of hyperpigmentation. She takes a holistic approach to skin rejuvenation, customizing each patient’s treatment plan to incorporate a combination of in-office treatment options and specially formulated skincare products tailored to their specific skin condition, concerns, and aesthetic goals.
What is melasma?
Melasma is a common and benign skin condition that results in dark patches of discoloration on the face and chest. It develops due to the overproduction of melanin by melanocytes in the skin. Melanocytes are the skin cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. When various contributing factors stimulate melanocytes, they produce excess pigment, which can lead to the development of melasma. Melasma primarily affects the upper lip, the bridge of the nose, the forehead, and the cheeks, often appearing symmetrically on both sides of the face. While it typically occurs on the face, melasma can also appear on areas such as the forearms, neck, and shoulders, particularly if they have been exposed to excessive sun or UV rays.
There are three main types of melasma: epidermal melasma, dermal melasma, and mixed melasma. In cases of epidermal melasma, pigmentation occurs in the top layer of the skin (along the skin’s surface), resulting in dark brown patches with well-defined borders. With dermal melasma, pigmentation appears as light brown or blue-gray, surrounded by a blurry border, and is more challenging to treat since it affects the dermal or middle layer of the skin. The most common form is mixed melasma, featuring bluish and brown patches of discoloration in both the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin.
Although melasma is not a harmful skin condition and does not necessarily increase patients’ risk of developing skin cancer, this form of pigmentation can make individuals feel self-conscious about their skin tone, significantly impacting their quality of life. While melasma cannot be cured, it can be effectively treated and managed through specific in-office treatments, topical skincare products, and lifestyle modifications. Melasma can be a challenging condition to treat, as some treatment options for pigmentation may actually worsen its appearance. It’s essential to have your melasma thoroughly examined by a board-certified dermatologist like Dr. Michele Green to determine the best treatment plan for your skin.
How can you diagnose melasma?
Melasma is typically diagnosed through a visual examination of the affected area, where pigmentation or skin discoloration is observed. A Wood’s lamp, an older diagnostic tool for melasma, uses specialized light to examine the condition in various dermal layers. Expert dermatologists, such as Dr. Green, can visually evaluate the area and identify the specific pattern of skin discoloration. Dr. Green has been treating patients with melasma for over 25 years and possesses extensive knowledge about this condition. For many patients, a visual examination suffices to diagnose this specific pattern of skin discoloration.
Who is prone to melasma?
Melasma can occur in any patient, but it is most common in women aged 20 to 40. While men can experience melasma, according to the American Academy of Dermatology, only 10% of individuals who develop this skin condition are men. Patients with darker skin, such as those of Latin/Hispanic, African, Mediterranean, or Middle Eastern descent, are statistically more likely to suffer from melasma. Although patients with lighter skin may develop melasma, it is often less noticeable compared to those with darker skin, especially individuals with brown skin. This is due to the higher concentration of melanocytes in darker skin.
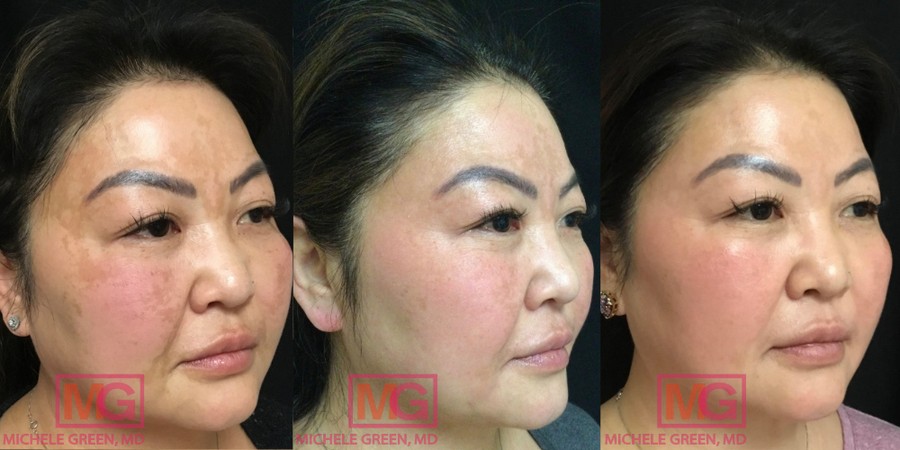
What causes melasma?
The exact causes of melasma remain unknown. Generally, melasma is caused by an increase in melanin produced by overactive melanocytes in the skin. The reason why these melanocytes are stimulated to produce an excess of melanin, leading to areas of concentrated pigment, is unclear. However, certain factors have been associated with the development of melasma, including genetics, hormonal fluctuations, specific medical conditions, and certain medications. When treating melasma, it is essential to understand what factors may contribute to its development. For some patients, addressing an underlying condition or changing medications can reduce the appearance of melasma or prevent its onset. During your consultation with Dr. Green, she will evaluate your medical history to determine the root cause of your melasma.
Does genetics cause melasma?
Many patients who struggle with melasma may have a genetic predisposition to the skin condition. It has been observed to run in families, with roughly one-third to one-half of melasma patients reporting that they have a family member who also suffers from the condition. Additionally, identical twins commonly share symptoms of melasma.
What hormone causes melasma?
Hormonal changes, particularly those involving the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone, are closely linked to the development of melasma. Research indicates that the use of birth control pills, pregnancy, and hormone replacement therapy can all trigger melasma flare-ups. Estrogen may increase melanin receptors in skin cells, making them more sensitive to sunlight and inflammation. Estrogen and progesterone are present in many birth control pills and hormone replacement therapies, and they also surge during pregnancy. This is also why melasma is often referred to as chloasma or the mask of pregnancy, due to the increased melanin and hyperpigmentation on the faces of pregnant women. In many cases, hormone-induced melasma diminishes once hormone levels stabilize. However, if it persists for more than three to six months postpartum or after discontinuing birth control, cosmetic treatments may be necessary.
Recent studies suggest that thyroid disease may be associated with the development of melasma. Hypothyroidism, a disorder characterized by an underactive thyroid, prevents the body from receiving normal hormone levels from the thyroid. This can result in hormonal imbalances, potentially leading to the development of melasma on the skin. Additionally, hyperthyroidism, a disorder marked by an overactive thyroid, also seems to influence melasma development. Although the exact mechanism behind melasma formation is unclear, these hormones can alter the production of inflammatory cytokines in the body, contributing to skin pigmentation.
Which medications cause melasma?
Certain medications have been shown to increase patients’ risk of developing melasma. Anti-seizure medications like Clobazam and Phenytoin are known to trigger or worsen melasma. Birth control pills containing estrogen and progesterone have been shown to elevate the risk of melasma. Other medications, including oral antibiotics, certain blood pressure drugs, and retinoids, heighten skin photosensitivity, increasing the likelihood of sun damage and melasma. If you notice the onset of melasma while taking any of these medications, consult your prescribing doctor to explore alternative treatments that can help prevent the progression of melasma.
What vitamin deficiencies cause melasma?
Although different nutritional deficiencies are not recognized as direct causes of melasma, some scientific evidence suggests that deficiencies in iron, vitamin D, and vitamin B12 may be linked to its development. For this reason, your healthcare provider may ask about your dietary habits to determine if any vitamin deficiencies could be an underlying factor in the pigmentation process.
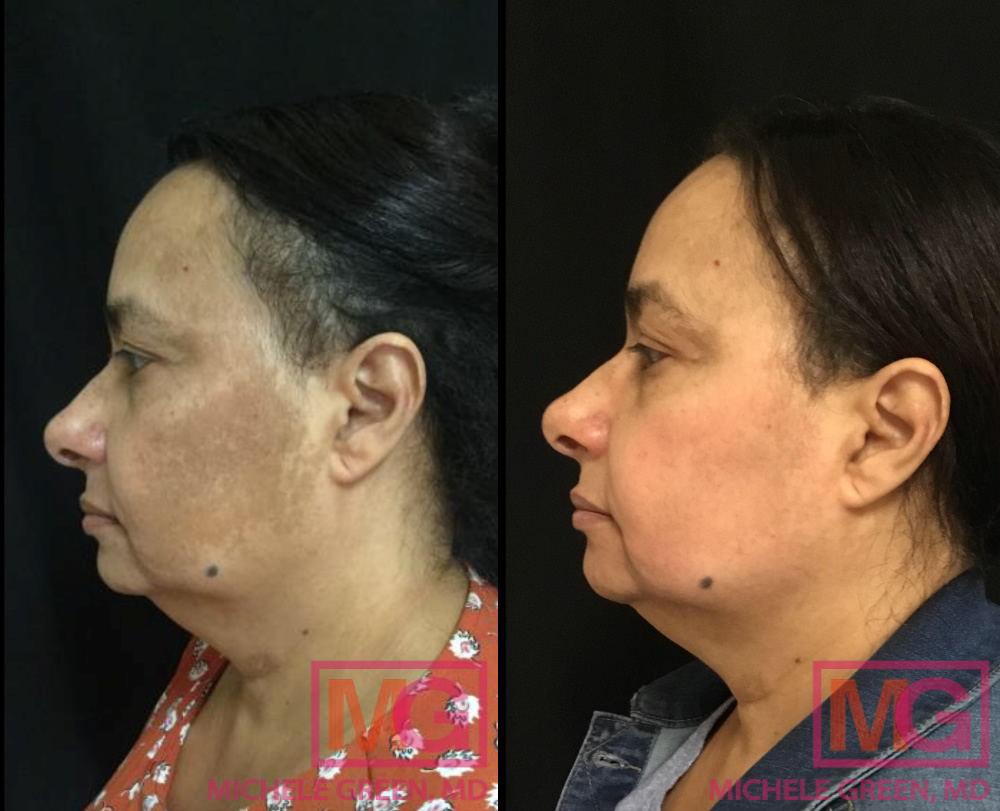
Cosmelan treatment for Melasma – before and after
Can stress cause melasma?
Sustained levels of stress can profoundly affect the body’s systems, negatively impacting sleep, digestion, and other bodily functions. When stressed, your body releases elevated amounts of the hormones cortisol and estrogen, which can trigger melasma. Chronic stress can also lead to skin damage and hinder healing. However, the full extent of stress’s impact on the onset of melasma has yet to be completely determined.
What foods aggravate melasma?
Melasma is not directly caused by food; however, certain dietary choices can influence its severity. High-glycemic index foods, such as sugar, white bread, and pastries, may worsen melasma by spiking insulin and disrupting hormone levels. Dairy products and soy-based foods can affect estrogen and progesterone levels, potentially worsening melasma in hormone-sensitive individuals. On the other hand, a diet rich in antioxidants, including berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits, along with foods high in vitamins C and E, omega-3 fatty acids (like fish and flaxseed), and minerals such as zinc and selenium, can support skin health and may help reduce the appearance of melasma.
Which cosmetic procedures are best for the treatment of melasma?
For many patients, in-office treatment options are the most effective method for reducing the appearance of melasma on the skin. Dr. Green offers a variety of non-invasive treatments that address melasma and are safe for patients of all skin types and tones. When you consult with Dr. Green at her private NYC dermatology practice, she will assess your melasma and skin concerns to select the most effective treatment for you. Often, a combination of in-office treatments and targeted skincare products is necessary to achieve optimal cosmetic results.
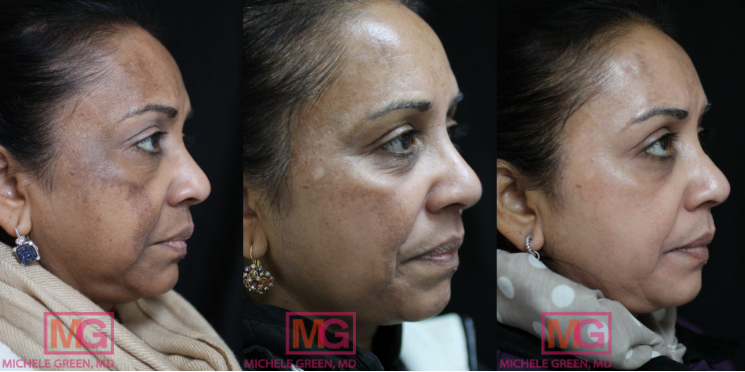
45-54 year old woman, Cosmelan treatment before and after
Cosmelan Peels to remove melasma
The Cosmelan peel is Dr. Green’s gold standard for treating melasma and hyperpigmentation. The Cosmelan peel is a professional-grade mask containing key tyrosinase inhibitors that block melanin production in the skin, complemented by other lightening agents to restore beautiful, clear skin. The mask is applied and left on for several hours, depending on your skin type and the extent of your hyperpigmentation or melasma. Patients are then instructed to remove the mask with a gentle cleanser and to use specially formulated creams to enhance the treatment results and continue lightening the pigmentation. Patients return to Dr. Green’s office four weeks later, where another application of the mask may be performed. The Cosmelan peel is an excellent treatment option for melasma, safe and effective for all skin types and tones, including those with darker skin tones. Many patients have achieved significant results from the Cosmelan peel; for many, Cosmelan is the only treatment that has been effective in addressing melasma.
Chemical Peels to treat melasma
Chemical peels are an excellent method for rejuvenating the skin and reducing hyperpigmentation and melasma. They use a chemical exfoliant to gently remove dead, pigmented skin cells, revealing healthy, bright skin beneath. Chemical peels come in various strengths and formulations, allowing for tailored treatment based on your skin type and the degree of pigmentation. In addition to treating melasma and hyperpigmentation, chemical peels can also improve acne scars, fine lines, and wrinkles. Patients with darker skin tones may not be ideal candidates for a chemical peel, depending on the strength and ingredients used, as adverse side effects can occur. Often, multiple treatment sessions spaced three to four weeks apart are needed to achieve the best cosmetic results.
Mesopeels for facial hyperpigmentation
Mesopeels are specially formulated chemical peels designed to address a wide variety of discoloration, hyperpigmentation, and melasma while helping to regulate melanocyte activity. They employ a process of chemo-exfoliation that not only revitalizes the skin’s surface like a traditional chemical peel but also stimulates the production of new collagen and elastin. Mesopeels are safe and gentle, suitable for application on various areas of the body in addition to the face. Unlike other types of chemical peels, Mesopeels can be used on patients with all skin types and tones, including darker skin tones. Generally, a series of four to six treatment sessions is necessary to achieve improvement on your facial hyperpigmentation.
Microneedling for melasma
Microneedling, also known as collagen induction therapy, involves using micro-needles to prick the skin’s surface, creating tiny micro-channels. By stimulating the body’s natural wound-healing process, microneedling can promote collagen production to diminish the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and uneven skin texture. Additionally, the micro-channels created in the skin improve the absorption of topical serums and gels. To treat melasma and other forms of hyperpigmentation, Dr. Green applies a depigmentation serum during the microneedling treatment. This serum is rich in skin-lightening ingredients, including tranexamic acid and vitamin C, which help reduce discoloration and create a more even skin tone. Multiple treatment sessions are necessary for addressing melasma and hyperpigmentation with microneedling.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a popular treatment option that mechanically exfoliates and removes the outer layer of dead skin cells using a handheld device. This method sprays aluminum oxide or sodium bicarbonate crystals while using vacuum suction to exfoliate the stratum corneum, the top layer of the skin. In addition to addressing melasma, microdermabrasion effectively treats fine lines, wrinkles, enlarged pores, sun damage, blackheads, acne, and acne scars, while also evening out skin tone and texture.
Hydrafacials to treat facial melasma
A HydraFacial is a three-step, 30-minute procedure that involves deep cleaning, gentle exfoliation, and the removal of impurities from your skin. The HydraFacial uses patented vortex technology to deeply penetrate the pores, enhancing cleansing and delivering targeted ingredients into the skin. The first step involves cleansing the skin to remove any superficial impurities. The second step involves exfoliating the pores to remove dead skin cells, dirt, excess oil, and other impurities. The final step delivers a high potency of nourishing vitamins and nutrients to hydrate and replenish the skin.
Additionally, the HydraFacial can be enhanced with skin boosters specifically designed to address concerns such as melasma, rosacea, acne, and dehydration. Two excellent boosters for melasma treatment are Britenol and Murad’s Vita-C Serum. The Britenol serum contains alpha-arbutin and vitamin C to brighten the skin while protecting it from free radical damage and oxidative stress. Murad’s Vita-C includes vitamin C as well as glycolic acid, tranexamic acid, and RepleniCell, a proprietary molecule from Murad that further reduces hyperpigmentation, hydrates the skin, and creates a more even skin tone.
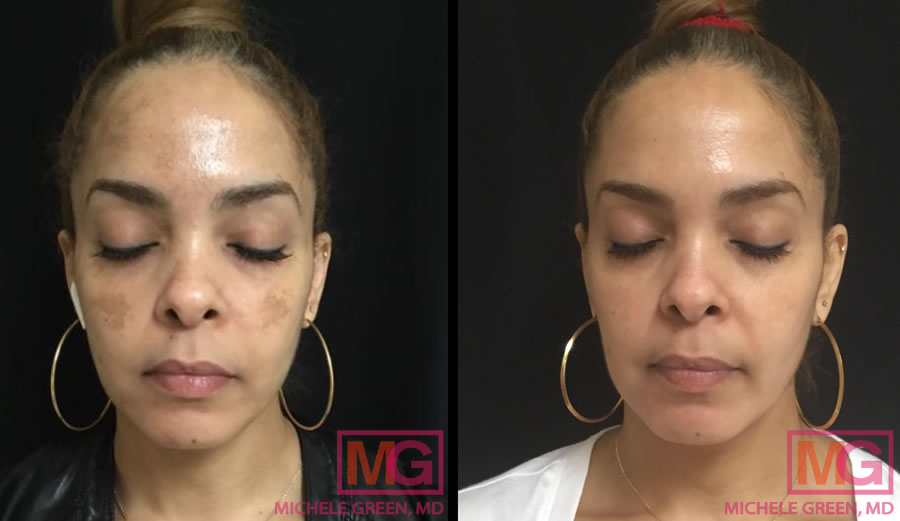

Cosmelan – 10 weeks before and after
Which topical skincare products best treat melasma and dark spots?
A proper skincare regimen is essential for patients with melasma, as targeted products can help lighten pigmentation, maintain treatment results, and prevent the condition from developing or worsening. Dr. Green will create a personalized skincare plan using specially formulated over-the-counter or prescription products, based on your skin type, tone, and severity of hyperpigmentation.
Sunscreen is critical when addressing melasma, as sun exposure can exacerbate the condition. Patients should apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 50 or higher to protect their skin from the sun’s harmful rays. Dr. Green recommends that melasma patients layer both a chemical and a physical sunscreen daily for optimal protection. Chemical sunscreens absorb UV rays, transforming them into heat and scattering them away from the skin. Common active ingredients found in chemical sunscreens include oxybenzone, azobenzene, octinoxate, and homosalate. Physical sunscreens, also known as mineral sunscreens, create a barrier on the skin that filters out and protects against harmful UV rays. Physical sunblocks usually contain titanium dioxide or zinc oxide. The Hydrating SPF 50 from Dr. Green’s proprietary skincare line, MGSKINLABs, is a mineral sunscreen that also incorporates hyaluronic acid and lactic acid to hydrate and soften the skin.
Hydroquinones are bleaching agents that lighten facial hyperpigmentation and melasma. Hydroquinone can only be obtained through a prescription from a board-certified dermatologist, like Dr. Michee Green in NYC, and should be used under a doctor’s supervision. Hydroquinones can be applied to the pigmented area for several months to improve the appearance of melasma. When using hydroquinone, it is essential to avoid sun exposure, as this product can increase the skin’s photosensitivity.
Retinoids and retinols are products derived from vitamin A that enhance collagen production and promote skin cell turnover. These products are commonly used to address various skin texture and discoloration issues, including melasma, sun spots, fine lines, wrinkles, and acne. Retinoids, such as tretinoin, require a prescription, whereas retinol is available over the counter. The Essential Antioxidant Infusion from MGSKINLABs is enriched with retinol, essential vitamins, and nutrients to exfoliate dead skin cells and nourish the skin for a brighter, smoother complexion. Like hydroquinones, retinoids can increase the skin’s sensitivity to sunlight and should only be used in conjunction with proper sun protection.
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that increases skin cell turnover and reduces discoloration, resulting in a brighter and more even skin tone. Its antioxidant properties also protect the skin from oxidative stress and free radical damage. Dr. Green’s MGSKINLABs has developed its vitamin C formulation, Vita-C Serum, designed to enhance cell renewal and collagen synthesis, minimizing the appearance of brown spots and improving skin texture.
Corticosteroids can only be safely used for a short duration in combination treatment, as topical steroid creams may thin the skin. They effectively lighten dark patches on the skin, including those caused by pigmentation from melasma.
Other effective skin-lightening ingredients for treating melasma include tranexamic acid, azelaic acid, and glycolic acid. MGSKINLAB’s Skin Brightening Cream features a unique blend of kojic acid, glycolic acid, lactic acid, and fruit extracts that gently lighten and diminish pigmentation on the skin.
How can I prevent melasma from occurring?
The best way to prevent melasma is by practicing proper sun protection. Patients should always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 50 or higher. Sunscreen must be used daily, even on cloudy days, because UV rays can penetrate through clouds, reflect off snow and puddles, and pass through windows. It’s crucial to reapply sunscreen every 90 minutes or after any water activities. Patients should wear a wide-brimmed hat, sunglasses, and sun-protective clothing to minimize sun exposure. If melasma develops due to specific medications, patients should consult their prescribing provider about alternatives that do not trigger or worsen melasma.
Does melasma ever go away?
In some cases, melasma can fade on its own. Melasma caused by certain medications or Pregnancy may disappear within a few months after stopping the medication or giving birth. However, for many people, melasma remains stubborn and does not resolve on its own. Although melasma is not curable, it can be effectively treated and managed through a combination of cosmetic procedures and topical skincare products. The Cosmelan peel is an incredibly effective in-office treatment that can significantly reduce melasma and restore a clear, even skin tone. Nonetheless, recurrence is always possible if patients do not maintain the results with proper sun protection and targeted skincare products. Dr. Green can advise on the best combination of treatments, topical medications, and skincare ingredients to help you eliminate melasma once and for all.
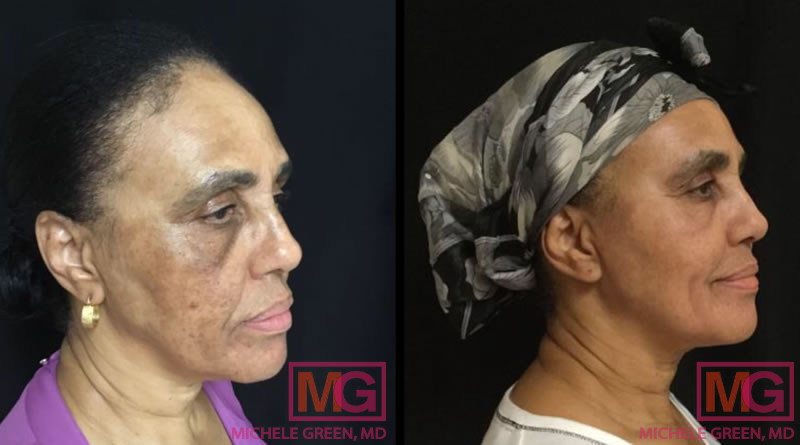
Cosmelan – 10 weeks before and after
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Melasma
Why do I suddenly have melasma?
Melasma typically develops gradually over time. However, various risk factors can trigger its sudden onset, including increased stress, certain medications, sun exposure, and hormonal fluctuations. If you notice new or worsening dark spots or patches on your skin, schedule a consultation with board-certified dermatologist Dr. Green, who has over 25 years of experience providing some of the world’s most discerning individuals with the best non-invasive treatment options for melasma. Whether your melasma has progressively worsened or appeared suddenly, Dr. Green will work with you to create a personalized treatment plan aimed at reducing the visibility of melasma and restoring a bright, even-toned complexion.
What triggers melasma?
The most common trigger for melasma is direct sun exposure. Ultraviolet light, including UVA and UVB rays, stimulates melanocytes to produce more melanin. Tanning beds are also known triggers for melasma, as they emit harmful UV rays and visible light that can stimulate melanocytes, exacerbate skin discoloration, and increase the risk of skin cancer. It is crucial to avoid the damaging effects of UV rays to prevent the recurrence of melasma after treatment. Even minimal sun or UV exposure can trigger a recurrence of melasma.
Is melasma cancerous?
No. Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by facial discoloration. It is a benign skin condition and not cancerous. Skin cancer is a serious disorder caused by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells. It can appear as dark spots on the skin and may resemble other forms of hyperpigmentation to the untrained eye. Suppose you are unsure whether your dark spots are due to hyperpigmentation, melasma, or skin cancer. In that case, it is best to schedule a consultation with a board-certified dermatologist, such as Dr. Green. In certain cases, it may be wise to perform a biopsy of the affected area. Skin conditions that are often mistaken for melasma include lichen planus and lentigines (age spots), among others. The biopsy will involve removing a small piece of the discolored skin for testing to rule out any more harmful skin conditions. The test results will also reveal the severity of the melasma, indicating its depth and extent. This way, more serious conditions, such as skin cancer, can be ruled out, and an appropriate treatment plan can be established.
What is the main cause of melasma?
Sadly, the primary cause of melasma remains unknown. Melasma occurs due to excessive melanin production by melanocytes in the epidermis. Sunlight and UV exposure can trigger or aggravate melasma, further encouraging melanocytes to produce melanin. Risk factors for developing melasma include genetics, hormonal imbalances, certain medications (e.g., oral antibiotics, antiseizure medications), and stress.
What causes facial melasma?
While patchy skin discoloration and dark spots linked to melasma can occur on any part of the body, they most commonly appear on the face. Melasma on the face can result from various risk factors, including sun exposure, use of tanning beds, hormonal fluctuations, and genetic predisposition. Melanocytes are skin cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. In melasma, when melanocytes produce excessive melanin, areas with surplus pigment develop as dark patches that are more pigmented than the surrounding skin. Melasma often appears on the face since it is one of the most sun-exposed areas of the body.
What causes melasma on the upper lip?
In many cases of melasma, a patient may notice that the skin discoloration characteristic of this condition appears above the upper lip. This specific form of melasma is commonly referred to as a “melasma mustache.” Typically, the factors that cause a melasma mustache are similar to those that lead to other cases of melasma on the face, including sun exposure, hormonal shifts, genetics, thyroid disease, and certain medications. A melasma mustache can be treated with the same topical and in-office procedures used for other melasma patches, providing relief for many patients dealing with this unwanted pigmentation.
What causes melasma in women?
Due to hormonal fluctuations, women are significantly more likely than men to develop melasma. Estrogen and progesterone are two hormones linked to the development of melasma. Women who use hormonal birth control or hormone replacement therapy often experience melasma and notice it fading when these medications are stopped. Additionally, melasma commonly appears during pregnancy due to increased hormone levels. Common risk factors for melasma development, including sun exposure, genetics, certain medications, and stress, can also contribute to the development of melasma in women.
What causes melasma in men?
It is estimated that only 10 percent of all melasma patients are men. Nevertheless, a range of environmental and biological risk factors can contribute to the development of melasma in men. Sun exposure acts as a major trigger, as ultraviolet (UV) light causes melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells, to increase melanin production. Furthermore, genetic factors are significant, as melasma often runs in families and is more common among individuals with darker skin tones. Other contributing factors may include heat, stress, certain medications, and cosmetic products that irritate the skin or heighten sun sensitivity. While men don’t develop melasma as frequently as women, Dr. Green treats both men and women with melasma at her private, boutique dermatology office on Manhattan’s Upper East Side, providing personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s skin type, tone, and severity of melasma.
What causes melasma in pregnancy?
For many pregnant women, the development of melasma can be a frustrating aspect of pregnancy. Often referred to as chloasma or the “mask of pregnancy,” melasma can occur due to elevated estrogen and progesterone levels, particularly during the third trimester. Fortunately, for most patients, pregnancy-induced melasma typically fades on its own after childbirth as hormone levels normalize. Additionally, if you’re experiencing melasma during pregnancy, there are safe and effective topical treatments, such as vitamin C, that can help reduce pigmented areas on the skin. If melasma persists for three to six months postpartum, it may indicate the need for cosmetic treatments like the Cosmelan peel to address the pigmentation fully.
What makes melasma worse?
UV radiation from sun exposure and tanning beds is the primary factor that can exacerbate melasma, as it prompts melanocytes to produce more melanin. When melanocytes are stimulated at varying rates, concentrated melanin may accumulate in specific areas of the face rather than others, eventually leading to melasma. This is why most individuals notice a worsening of their melasma symptoms during the summer months. To reduce melasma caused by UV exposure, patients should utilize adequate sun protection, including sunscreen and wide-brimmed hats. Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in estrogen, can also aggravate melasma, as they can similarly stimulate the melanocytes in the skin to produce more pigment. This explains why pregnant women and those using oral contraceptives are at a higher risk of developing melasma.
Other factors that can exacerbate melasma include certain anti-seizure medications, phototoxic drugs, and hypothyroidism. Additionally, some over-the-counter skincare products, especially harsh exfoliants and photosensitizing agents, can worsen the appearance of melasma. If you notice changes in your skin shortly after starting a new product or medication, it might indicate that it is triggering your melasma. By identifying your triggers and practicing sun protection, you can help prevent your melasma from worsening or recurring.
Can lasers treat melasma?
No, laser treatment for melasma is not recommended. Lasers like IPL, Fraxel, and Picosure effectively treat other forms of pigmentation, including sun spots, age spots, and freckles. However, when applied to melasma, the heat from these lasers can “burn the pigmentation,” causing the melasma to become more entrenched in the deeper layers of the skin, making it much harder to remove. Dr. Green often sees patients who have tried to treat pigmentation with lasers, and in many cases, these treatments can worsen the appearance of melasma. Dr. Green prefers to treat melasma with gentle peels, such as the Cosmelan peel or Mesopeels, to minimize the exacerbation of existing hyperpigmentation. Dr. Green understands the importance of accurately diagnosing and effectively treating pigmentation the first time, with the safety and satisfaction of her patients being her top priorities.
Why does my melasma keep coming back?
Melasma is a chronic skin disorder associated with various underlying causes. In some cases, the dark patches may fade naturally once the cause is treated. However, most patients with melasma require intervention to fully resolve the hyperpigmentation, which may involve targeted topical treatments and non-invasive cosmetic procedures such as the Cosmelan peel. Melasma can recur even after treatment if patients fail to practice proper sun protection. During and after melasma treatment, patients must exercise extreme caution in the sun, as any exposure can trigger a recurrence of the condition. A broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 50 should be applied to guard against both UVA and UVB rays. For optimal protection, Dr. Green recommends that her patients use two types of sunscreen: layering a chemical sunscreen beneath a physical sunscreen for the best defense.
Additionally, melasma may recur due to certain medications. Melasma can be a challenging skin condition to treat and manage. Trusting an experienced expert to develop your treatment plan is the most effective, efficient, and safest way to achieve a clear complexion while maintaining beautiful, youthful-looking skin in the long term. Dr. Green has over two decades of experience in treating melasma and hyperpigmentation in patients of all skin types and tones. She dedicates time to customizing your melasma treatment plan to address your specific skin concerns and aesthetic goals. Moreover, she will create a personalized skincare regimen and discuss any necessary lifestyle changes to help you keep your melasma at bay for good.
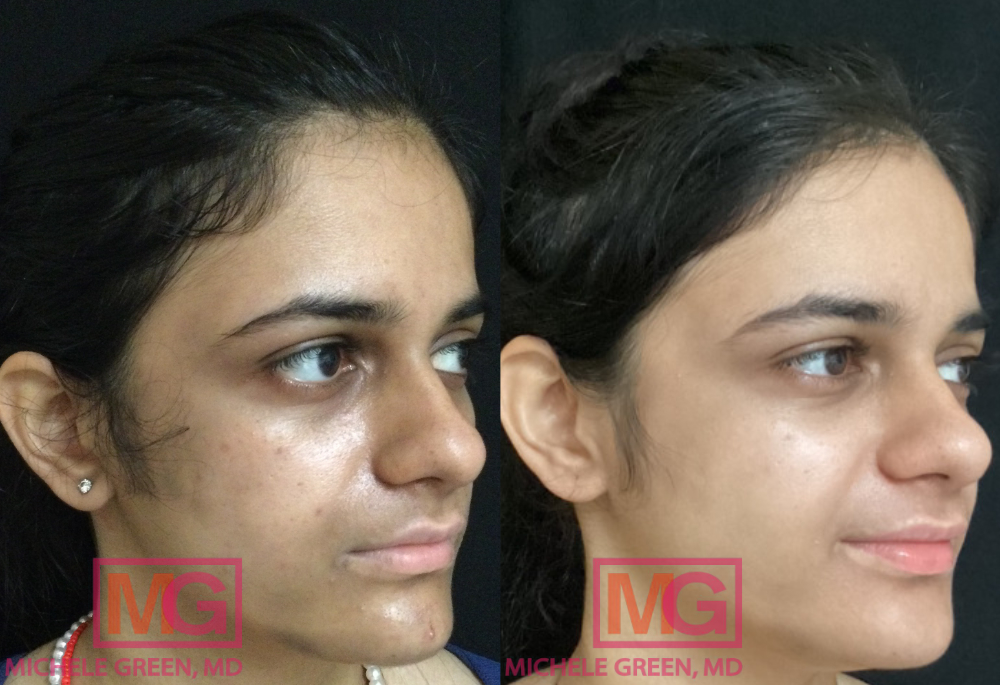

How do I get started with the best melasma treatment today?
Although melasma is a benign skin condition, the presence of patchy skin discoloration and dark spots can evoke self-conscious feelings about one’s appearance for many individuals. Numerous factors can contribute to the development of melasma, and understanding these causes is essential for effectively treating and managing its symptoms. Dr. Green has extensive experience in treating melasma and creates customized treatment plans for each patient, taking into account their specific skin type, tone, and the severity of the condition. Melasma can be challenging to treat and manage effectively, with the most successful treatment plans typically involving a combination of non-invasive cosmetic procedures and specially formulated topical treatments. If you are troubled by dark patches related to melasma, Dr. Green is here to help.
Dr. Michele Green is an internationally renowned, board-certified cosmetic dermatologist with over 25 years of experience providing some of the world’s most discerning clients with the finest non-invasive treatment options for melasma, including Cosmelan peels, Mesopeels, and microneedling. Dr. Green adopts a holistic approach and adheres to a less-is-more philosophy regarding facial rejuvenation, tailoring each patient’s treatment plan to address their unique concerns and aesthetic goals. She is consistently recognized as one of New York City’s top dermatologists by Castle Connolly, New York Magazine, Super Doctors, and The New York Times for her dedication to patient care and expertise. If you are seeking the best melasma treatment in New York, please call our office at 212-535-3088 or contact us online to schedule a consultation and get started developing your customized treatment plan with Dr. Green today.
 212-535-3088
212-535-3088